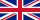
Acid Black 1 - CAS 1064-48-8 Acid black 2 (Nigrosine) - CAS 8005-03-6 Acid blue 258 (Tectilon Blue 6G) - CAS 61847-68-5 Acid Green 16 - CAS 12768-78-4 Acid Red 26 - CAS 3761-53-3 Acid red 42 (Rouge Tectilon 4B) - CAS 6245-60-9 Acid Violet 17 - CAS 4129-84-4 Acid Violet 49 - CAS 1694-09-3 Acid Yellow 36 - CAS 587-98-4 Acid yellow 169 (Jaune Tectilon 2G) - CAS 12220-88-1 Basic Blue 7 - CAS 2390-60-5 Basic Green 1 (brilliant green) - CAS 633-03-4 Basic Red 1 - CAS 989-38-8 Basic Red 9 - CAS 569-61-9 Basic Violet 1 - CAS 8004-87-3 Azorubine Red / Carmoisine (E122) - CAS 3567-69-9 Ponceau 4R or Cochineal Red A (E124) - CAS 2611-82-7 | Basic Violet 10 (rhodamine b) - CAS 81-88-9 Basic Violet 3 - CAS 548-62-9 Disperse Blue 1 - CAS 2475-45-8 Disperse Blue 106 - CAS 12223-01-7 Disperse Blue 124 - CAS 61951-51-7 Disperse Blue 3 - CAS 2475-46-9 Disperse Blue 35 - CAS 12222-75-2 Disperse Orange 3 - CAS 730-40-5 Disperse Orange 37 - CAS 12223-33-5 Disperse Red 1 - CAS 2872-52-8 Disperse Red 17 - CAS 3179-89-3 Disperse Yellow 3 - CAS 2832-40-8 Disperse Yellow 9 - CAS 6373-73-5 Pigment Orange 5 - CAS 3468-63-1 Pigment Red 53 - CAS 2092-56-0 Red Allura AC (E 129) - CAS 25956-17-6 Brilliant blue FCF (Xylene blue VSG or Erioglaucine or E 133)
CAS 2650-18-2; 3844-45-9 | Pigment Red 57-1 (Lithol rubine BK) - CAS 5281-04-9 Pigment red 122 - CAS 980-26-7 Pigment red 170 - CAS 2786-76-7 Pigment Violet 3 - CAS 1325-82-2 Pigment Yellow 13 - CAS 5102-83-0; 6358-85-6 Pigment Yellow 83 - CAS 5567-15-7 Solvent black 5 (Nigrosine) - CAS 11099-03-9 Solvent Blue 35 (Sudan blue 2) - CAS 17354-14-2 Solvent Orange 7 (Sudan II) - CAS 3118-97-6 Solvent Red 24 (Sudan IV) - CAS 85-83-6 Solvent Red 49 - CAS 509-34-2 Solvent Violet 9 - CAS 467-63-0 Solvent Yellow 2 (butter yellow, dimethyl yellow) - CAS 60-11-7 Tartrazine yellow (E 102) - CAS 1934-21-0; 12225-21-7 Quinoline yellow (E 104) - CAS 8004-92-0 Orange yellow (E110) - CAS 2783-94-0 Patent blue V (E 131) - CAS 3536-49-0 Food brown 3 (E 155) - CAS 4553-89-3 |

 EN
EN
 FR
FR