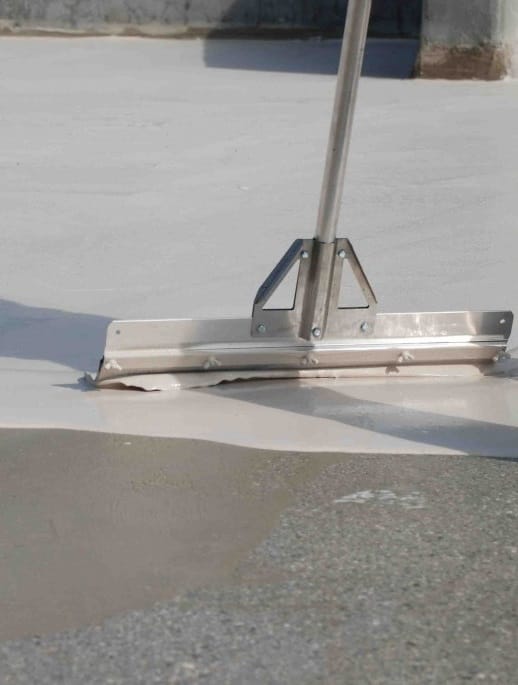
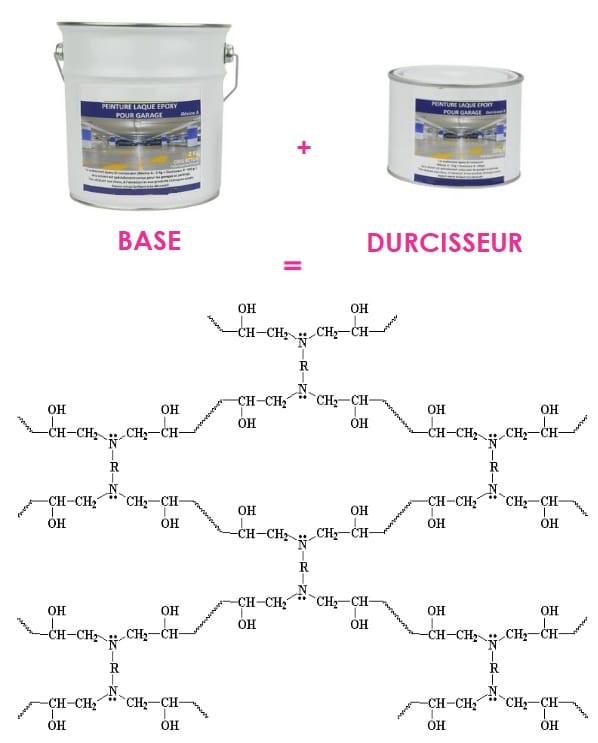
Stoichiometric defect on a Base/Hardener epoxy bicomponent mixture
A large crack appeared on a parking surface. This coating, however recent, probably presents a major failure .
What if a stoichiometric problem was the cause of this disorder?
Two-component epoxy resins, or also called epoxy polymers and more commonly "epoxy", are formed by polymerization of epoxy monomers with a hardener (crosslinking agent) to form three-dimensional polymers.
After polymerization, as soon as the mixture is "dry"; the polymer becomes rigid and retains its shape to form a practically inert material.
Respecting the base and hardener stochiometry is essential for the good performance of the material. Indeed, the adhesion properties of such systems are directly proportional to the quality of compliance with this ratio.

 EN
EN
 FR
FR