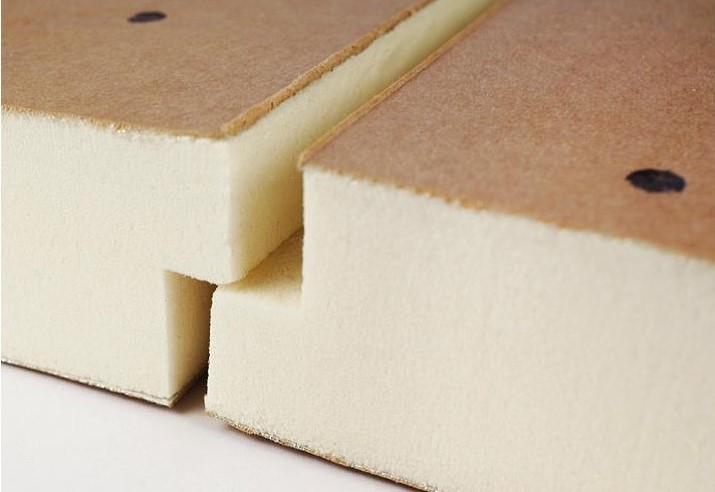
Polyurethane foam is produced by adding a blowing agent such as Carbon dioxide, Methylene chloride [75-09-2], Alkanes (Isobutane [75-28-5], Butane [106-97- 8]…), Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) such as Polyfluoropropane [679-86-7], [431-63-0], [690-39-1], Polyfluorobutane [406-58-6], Hydrofluoro-olefins (HFO) such as Polyfluoropropene [1645-83-6] ...
These gases present in the design of the foam will gradually escape from the cells of the foam to make room for air. A foam which will have completely degassed will contain no more (or very little) of these blowing agents.

 EN
EN
 FR
FR

