BIOSOURCED POLYOLS
Biosourced raw materials, that is to say from renewable resources, are on the rise for obvious economic (cost reduction),
ecological (reduction of greenhouse gas emissions), environmental and political reasons.
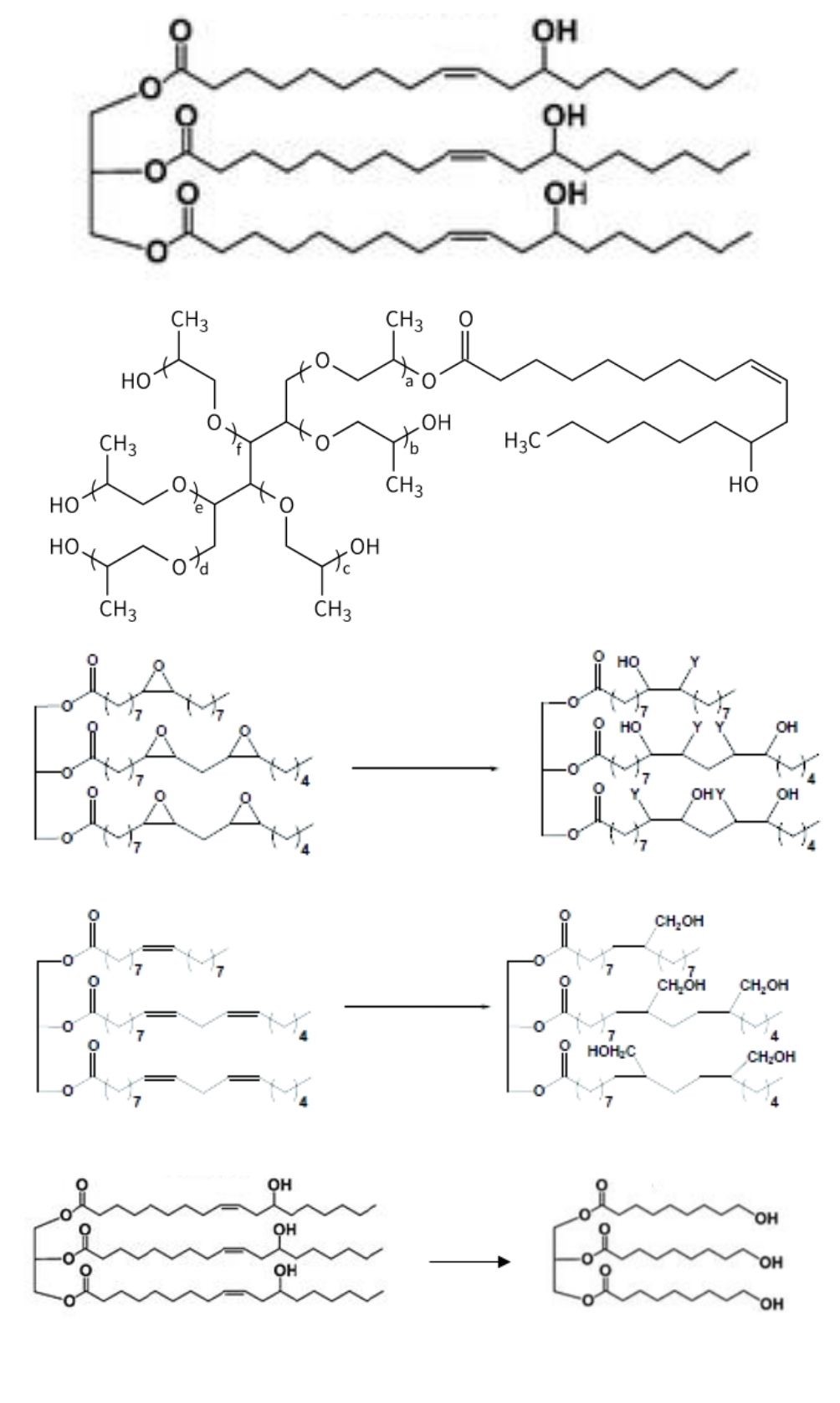
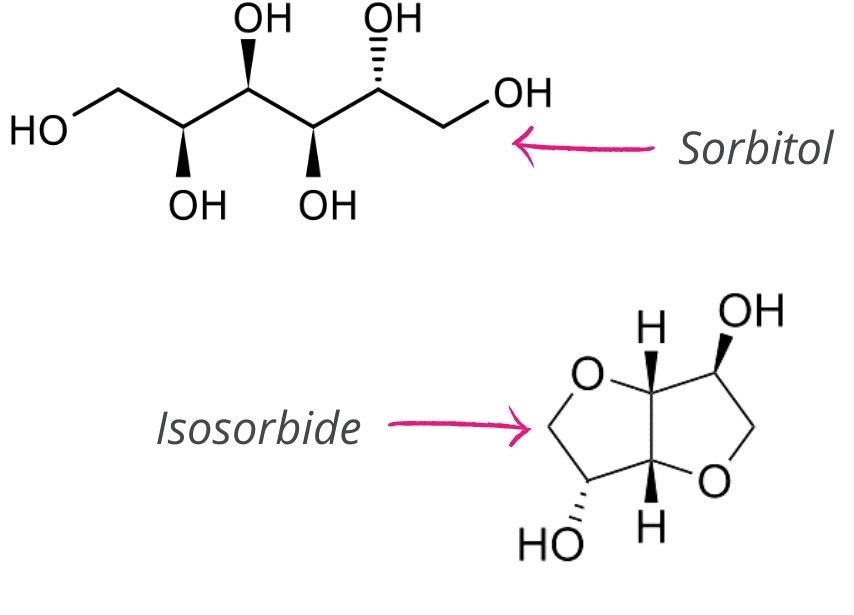
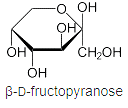
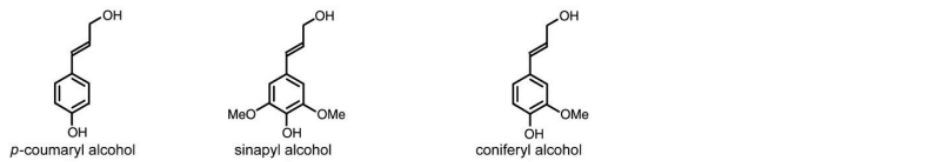
Vegetable oils, starch, sugars, cellulose and lignin are the main bio-sourced raw materials and are already present in many sectors such as energy,
industry , fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals,
cosmetics and food. They are transformed (via chemical reactions) into polyols which are then used for many applications, including the
synthesis of bio-based polymers .

 EN
EN
 FR
FR